Amazon Aurora
Overview
This service contains code to deploy an Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) cluster that can run Amazon Aurora, Amazon’s cloud-native relational database. The cluster is managed by AWS and automatically handles standby failover, read replicas, backups, patching, and encryption.
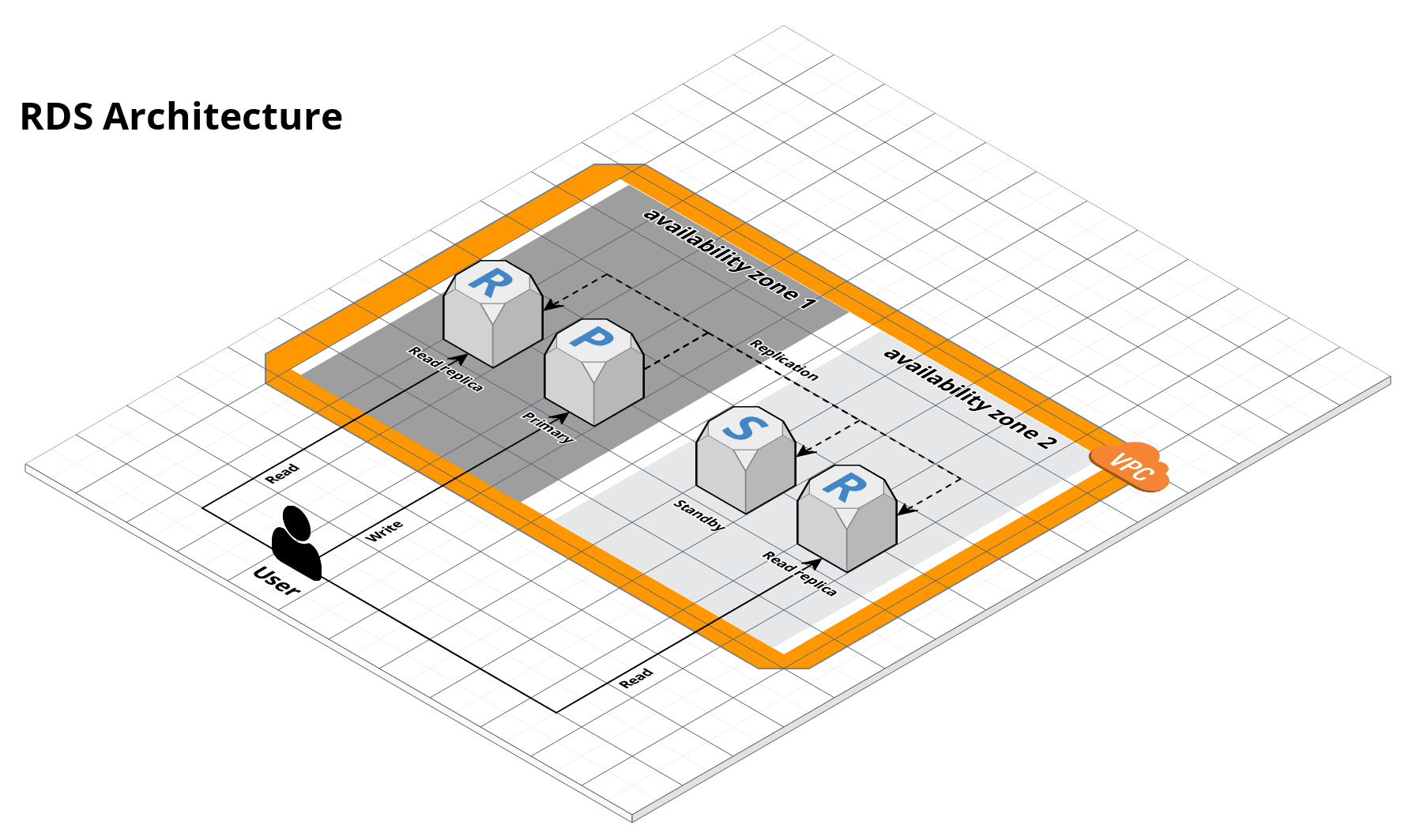 RDS architecture
RDS architecture
Features
- Deploy a fully-managed, cloud-native relational database
- MySQL and PostgreSQL compatibility
- Automatic failover to a standby in another availability zone
- Read replicas
- Automatic nightly snapshots
- Automatic cross account snapshots
- Automatic scaling of storage
- Scale to 0 with Aurora Serverless
- Integrate with Kubernetes Service Discovery
Learn
note
This repo is a part of the Gruntwork Service Catalog, a collection of reusable, battle-tested, production ready infrastructure code. If you’ve never used the Service Catalog before, make sure to read How to use the Gruntwork Service Catalog!
- What is Amazon RDS?
- Common gotchas with RDS
- Aurora Serverless documentation: Amazon’s docs for Aurora Serverless, including its advantages, limitations, architecture, and scaling configurations.
- RDS documentation: Amazon’s docs for RDS that cover core concepts such a the types of databases supported, security, backup & restore, and monitoring.
- Designing Data Intensive Applications: the best book we’ve found for understanding data systems, including relational databases, NoSQL, replication, sharding, consistency, and so on.
Deploy
Non-production deployment (quick start for learning)
If you just want to try this repo out for experimenting and learning, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-learning-and-testing folder: The
examples/for-learning-and-testingfolder contains standalone sample code optimized for learning, experimenting, and testing (but not direct production usage).
Production deployment
If you want to deploy this repo in production, check out the following resources:
- examples/for-production folder: The
examples/for-productionfolder contains sample code optimized for direct usage in production. This is code from the Gruntwork Reference Architecture, and it shows you how we build an end-to-end, integrated tech stack on top of the Gruntwork Service Catalog.
Reference
- Inputs
- Outputs
Required
aurora_subnet_idslist(required)The list of IDs of the subnets in which to deploy Aurora. The list must only contain subnets in vpc_id.
list(string)
namestring(required)The name used to namespace all the Aurora resources created by these templates, including the cluster and cluster instances (e.g. drupaldb). Must be unique in this region. Must be a lowercase string.
vpc_idstring(required)The ID of the VPC in which to deploy Aurora.
Optional
alarms_sns_topic_arnslist(optional)The ARNs of SNS topics where CloudWatch alarms (e.g., for CPU, memory, and disk space usage) should send notifications. Also used for the alarms if the share snapshot backup job fails.
list(string)
[]allow_connections_from_cidr_blockslist(optional)The list of network CIDR blocks to allow network access to Aurora from. One of allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the database to be reachable.
list(string)
[]allow_connections_from_security_groupslist(optional)The list of IDs or Security Groups to allow network access to Aurora from. All security groups must either be in the VPC specified by vpc_id, or a peered VPC with the VPC specified by vpc_id. One of allow_connections_from_cidr_blocks or allow_connections_from_security_groups must be specified for the database to be reachable.
list(string)
[]allow_major_version_upgradebool(optional)Enable to allow major engine version upgrades when changing engine versions.
falseapply_immediatelybool(optional)Specifies whether any cluster modifications are applied immediately, or during the next maintenance window. Note that cluster modifications may cause degraded performance or downtime.
falsebackup_job_alarm_periodnumber(optional)How often, in seconds, the backup job is expected to run. This is the same as schedule_expression, but unfortunately, Terraform offers no way to convert rate expressions to seconds. We add a CloudWatch alarm that triggers if the metric in create_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespace isn't updated within this time period, as that indicates the backup failed to run.
3600backup_retention_periodnumber(optional)How many days to keep backup snapshots around before cleaning them up. Max: 35
30copy_tags_to_snapshotbool(optional)Copy all the Aurora cluster tags to snapshots. Default is false.
falsecreate_snapshot_cloudwatch_metric_namespacestring(optional)The namespace to use for the CloudWatch metric we report every time a new RDS snapshot is created. We add a CloudWatch alarm on this metric to notify us if the backup job fails to run for any reason. Defaults to the cluster name.
nullcustom_tagsmap(optional)A map of custom tags to apply to the RDS cluster and all associated resources created for it. The key is the tag name and the value is the tag value.
map(string)
{}dashboard_cpu_usage_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the cpu usage widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
dashboard_db_connections_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the database connections widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
dashboard_disk_space_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the available disk space widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
dashboard_memory_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the available memory widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
dashboard_read_latency_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
dashboard_write_latency_widget_parametersobject(optional)Parameters for the read latency widget to output for use in a CloudWatch dashboard.
object({
# The period in seconds for metrics to sample across.
period = number
# The width and height of the widget in grid units in a 24 column grid. E.g., a value of 12 will take up half the
# space.
width = number
height = number
})
{
height = 6,
period = 60,
width = 8
}
db_cluster_custom_parameter_groupobject(optional)Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB cluster. This will create a new parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be launched with the default parameter group.
object({
# Name of the parameter group to create
name = string
# The family of the DB cluster parameter group.
family = string
# The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
parameters = list(object({
# Parameter name to configure.
name = string
# Vaue to set the parameter.
value = string
# When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
apply_method = string
}))
})
nulldb_config_secrets_manager_idstring(optional)The friendly name or ARN of an AWS Secrets Manager secret that contains database configuration information in the format outlined by this document: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/secretsmanager/latest/userguide/best-practices.html. The engine, username, password, dbname, and port fields must be included in the JSON. Note that even with this precaution, this information will be stored in plaintext in the Terraform state file! See the following blog post for more details: https://blog.gruntwork.io/a-comprehensive-guide-to-managing-secrets-in-your-terraform-code-1d586955ace1. If you do not wish to use Secrets Manager, leave this as null, and use the master_username, master_password, db_name, engine, and port variables.
nulldb_instance_custom_parameter_groupobject(optional)Configure a custom parameter group for the RDS DB Instance. This will create a new parameter group with the given parameters. When null, the database will be launched with the default parameter group.
object({
# Name of the parameter group to create
name = string
# The family of the DB cluster parameter group.
family = string
# The parameters to configure on the created parameter group.
parameters = list(object({
# Parameter name to configure.
name = string
# Vaue to set the parameter.
value = string
# When to apply the parameter. "immediate" or "pending-reboot".
apply_method = string
}))
})
nulldb_namestring(optional)The name for your database of up to 8 alpha-numeric characters. If you do not provide a name, Amazon RDS will not create a database in the DB cluster you are creating. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id. A value here overrides the value in db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullenable_cloudwatch_alarmsbool(optional)Set to true to enable several basic CloudWatch alarms around CPU usage, memory usage, and disk space usage. If set to true, make sure to specify SNS topics to send notifications to using alarms_sns_topic_arn.
trueenable_cloudwatch_metricsbool(optional)When true, enable CloudWatch metrics for the manual snapshots created for the purpose of sharing with another account.
trueenable_deletion_protectionbool(optional)Enable deletion protection on the database instance. If this is enabled, the database cannot be deleted.
falseenable_perf_alarmsbool(optional)Set to true to enable alarms related to performance, such as read and write latency alarms. Set to false to disable those alarms if you aren't sure what would be reasonable perf numbers for your RDS set up or if those numbers are too unpredictable.
trueenable_share_snapshot_cloudwatch_alarmsbool(optional)When true, enable CloudWatch alarms for the manual snapshots created for the purpose of sharing with another account. Only used if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
trueenabled_cloudwatch_logs_exportslist(optional)If non-empty, the Aurora cluster will export the specified logs to Cloudwatch. Must be zero or more of: audit, error, general and slowquery
list(string)
[]enginestring(optional)The name of the database engine to be used for this DB cluster. Valid Values: aurora (for MySQL 5.6-compatible Aurora), aurora-mysql (for MySQL 5.7-compatible Aurora), and aurora-postgresql. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id. A value here overrides the value in db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullengine_modestring(optional)The version of aurora to run - provisioned or serverless.
provisionedengine_versionstring(optional)The Amazon Aurora DB engine version for the selected engine and engine_mode. Note: Starting with Aurora MySQL 2.03.2, Aurora engine versions have the following syntax <mysql-major-version>.mysql_aurora.<aurora-mysql-version>. e.g. 5.7.mysql_aurora.2.08.1.
nullhigh_cpu_utilization_periodnumber(optional)The period, in seconds, over which to measure the CPU utilization percentage.
60high_cpu_utilization_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the DB instance has a CPU utilization percentage above this threshold.
90high_read_latency_periodnumber(optional)The period, in seconds, over which to measure the read latency.
60high_read_latency_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the DB instance read latency (average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
5high_write_latency_periodnumber(optional)The period, in seconds, over which to measure the write latency.
60high_write_latency_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the DB instance write latency (average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation), in seconds, is above this threshold.
5iam_database_authentication_enabledbool(optional)Specifies whether mappings of AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) accounts to database accounts is enabled. Disabled by default.
falseinstance_countnumber(optional)The number of DB instances, including the primary, to run in the RDS cluster. Only used when engine_mode is set to provisioned.
1instance_typestring(optional)The instance type to use for the db (e.g. db.r3.large). Only used when engine_mode is set to provisioned.
db.t3.smallkms_key_arnstring(optional)The ARN of a KMS key that should be used to encrypt data on disk. Only used if storage_encrypted is true. If you leave this null, the default RDS KMS key for the account will be used.
nulllow_disk_space_available_periodnumber(optional)The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free disk space.
60low_disk_space_available_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the amount of disk space, in Bytes, on the DB instance drops below this threshold.
1000000000low_memory_available_periodnumber(optional)The period, in seconds, over which to measure the available free memory.
60low_memory_available_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the amount of free memory, in Bytes, on the DB instance drops below this threshold.
100000000master_passwordstring(optional)The value to use for the master password of the database. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id. A value here overrides the value in db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullmaster_usernamestring(optional)The value to use for the master username of the database. This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id. A value here overrides the value in db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullportnumber(optional)The port the DB will listen on (e.g. 3306). This can also be provided via AWS Secrets Manager. See the description of db_config_secrets_manager_id. A value here overrides the value in db_config_secrets_manager_id.
nullpublicly_accessiblebool(optional)If you wish to make your database accessible from the public Internet, set this flag to true (WARNING: NOT RECOMMENDED FOR REGULAR USAGE!!). The default is false, which means the database is only accessible from within the VPC, which is much more secure. This flag MUST be false for serverless mode.
falserestore_source_cluster_identifierstring(optional)If non-empty, the Aurora cluster will be restored from the given source cluster using the latest restorable time. Can only be used if snapshot_identifier is null. For more information see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/AuroraUserGuide/USER_PIT.html
nullrestore_typestring(optional)Only used if 'restore_source_cluster_identifier' is non-empty. Type of restore to be performed. Valid options are 'full-copy' and 'copy-on-write'. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/AuroraUserGuide/Aurora.Managing.Clone.html
nullscaling_configuration_auto_pausebool(optional)Whether to enable automatic pause. A DB cluster can be paused only when it's idle (it has no connections). If a DB cluster is paused for more than seven days, the DB cluster might be backed up with a snapshot. In this case, the DB cluster is restored when there is a request to connect to it. Only used when engine_mode is set to serverless.
truescaling_configuration_max_capacitynumber(optional)The maximum capacity. The maximum capacity must be greater than or equal to the minimum capacity. Valid capacity values are 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256. Only used when engine_mode is set to serverless.
256scaling_configuration_min_capacitynumber(optional)The minimum capacity. The minimum capacity must be lesser than or equal to the maximum capacity. Valid capacity values are 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256. Only used when engine_mode is set to serverless.
2scaling_configuration_seconds_until_auto_pausenumber(optional)The time, in seconds, before an Aurora DB cluster in serverless mode is paused. Valid values are 300 through 86400. Only used when engine_mode is set to serverless.
300share_snapshot_max_snapshotsnumber(optional)The maximum number of snapshots to keep around for the purpose of cross account sharing. Once this number is exceeded, a lambda function will delete the oldest snapshots. Only used if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
30share_snapshot_schedule_expressionstring(optional)An expression that defines how often to run the lambda function to take snapshots for the purpose of cross account sharing. For example, cron(0 20 * ? ) or rate(5 minutes). Required if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true
nullshare_snapshot_with_account_idstring(optional)The ID of the AWS Account that the snapshot should be shared with. Required if share_snapshot_with_another_account is true.
nullshare_snapshot_with_another_accountbool(optional)If set to true, take periodic snapshots of the Aurora DB that should be shared with another account.
falseskip_final_snapshotbool(optional)Determines whether a final DB snapshot is created before the DB instance is deleted. Be very careful setting this to true; if you do, and you delete this DB instance, you will not have any backups of the data! You almost never want to set this to true, unless you are doing automated or manual testing.
falsesnapshot_identifierstring(optional)If non-null, the RDS Instance will be restored from the given Snapshot ID. This is the Snapshot ID you'd find in the RDS console, e.g: rds:production-2015-06-26-06-05.
nullstorage_encryptedbool(optional)Specifies whether the DB cluster uses encryption for data at rest in the underlying storage for the DB, its automated backups, Read Replicas, and snapshots. Uses the default aws/rds key in KMS.
truetoo_many_db_connections_thresholdnumber(optional)Trigger an alarm if the number of connections to the DB instance goes above this threshold.
nullA list of all the CloudWatch Dashboard metric widgets available in this module.
The ARN of the AWS Lambda Function used for cleaning up manual snapshots taken for sharing with secondary accounts.
The ARN of the RDS Aurora cluster.
The ID of the RDS Aurora cluster (e.g TODO).
The unique resource ID assigned to the cluster e.g. cluster-POBCBQUFQC56EBAAWXGFJ77GRU. This is useful for allowing database authentication via IAM.
The ARN of the AWS Lambda Function used for periodically taking snapshots to share with secondary accounts.
A list of endpoints of the RDS instances that you can use to make requests to.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs CPU usage (percentage) of the Aurora cluster.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the number of active database connections of the Aurora cluster.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs available disk space (in bytes) on the Aurora cluster.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs available memory (in bytes) on the Aurora cluster.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation on reads.
A CloudWatch Dashboard widget that graphs the average amount of time taken per disk I/O operation on writes.
The port used by the RDS Aurora cluster for handling database connections.
The primary endpoint of the RDS Aurora cluster that you can use to make requests to.
The host portion of the Aurora endpoint. primary_endpoint is in the form '<host>:<port>', and this output returns just the host part.
A read-only endpoint for the Aurora cluster, automatically load-balanced across replicas.
The ARN of the AWS Lambda Function used for sharing manual snapshots with secondary accounts.